Implicit Differentiation
Differentiation of an equation in which the dependent variable doesn't have a side of the equation all to itself.
Derivative Of A Function
The measurement of how
f(
x) changes at a point
x.
Slope Of A Line
The change in the
y-value of the line for a unit change in the
x value.
Average Rate Of Change
The change in the function
f(
x) as
x changes over an interval [
a,
b].
Instantaneous Rate Of Change
The change in the function
f(
x) at a point
x.
Secant Line
A line joining two points on the graph of a function.
Tangent Line
A line that touches the graph of a function
f(
x) at a point.
Differentiability
If the limit
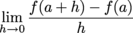
exists, the function
f(
x) is differentiable at
x =
a.
Vector
A mathematical structure that has both magnitude and direction, represented by an ordered pair of components.
Magnitude Of A Vector
The length of a vector, denoted by || ||.
Direction Of A Vector
The counter-clockwise angle from the positive
x-axis to the vector.
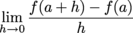 exists, the function f(x) is differentiable at x = a.
exists, the function f(x) is differentiable at x = a.