ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
AP Physics 1 Videos 86 videos
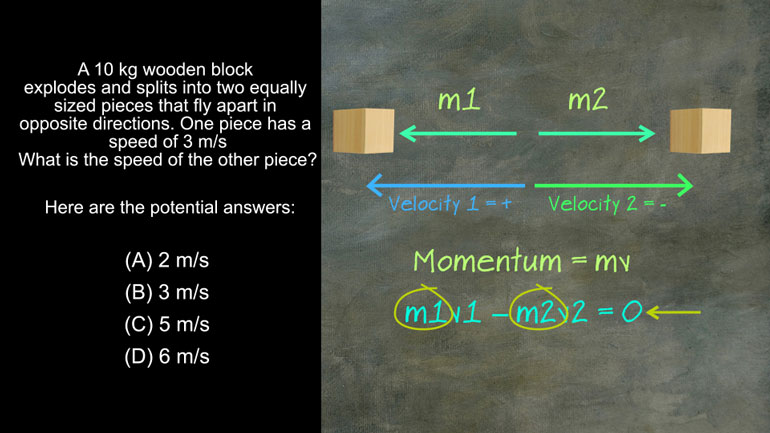
AP Physics 1: 2.5 Changes and Conservation Law. At what point(s) in this situation is energy lost in any form?
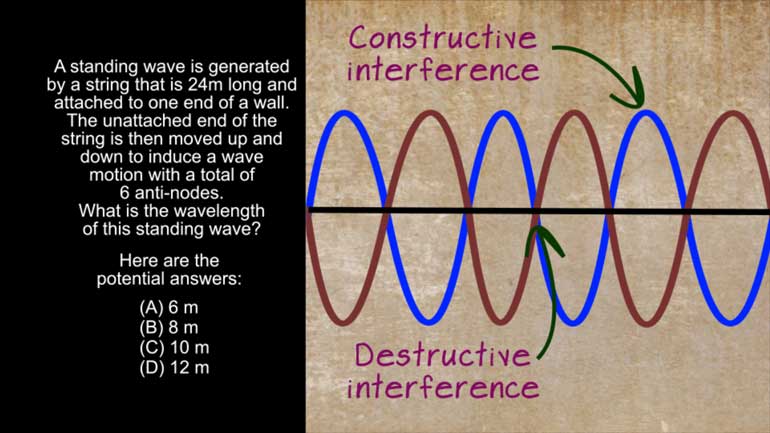
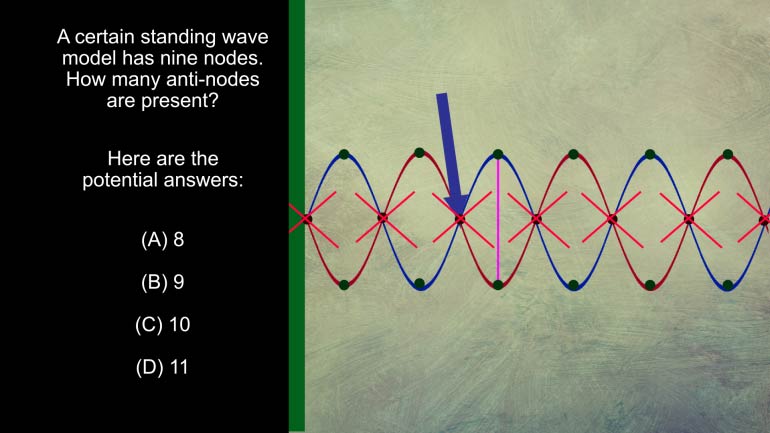
AP Physics 1: 1.4 Waves. Which of the following is technically true for Max as he stands at the edge of oblivion?
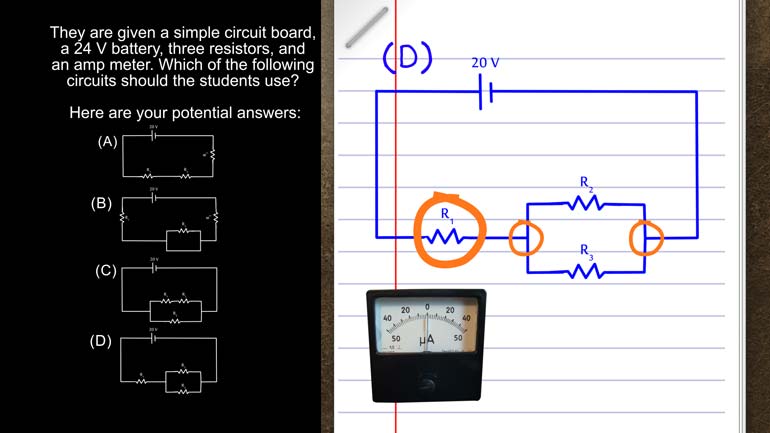
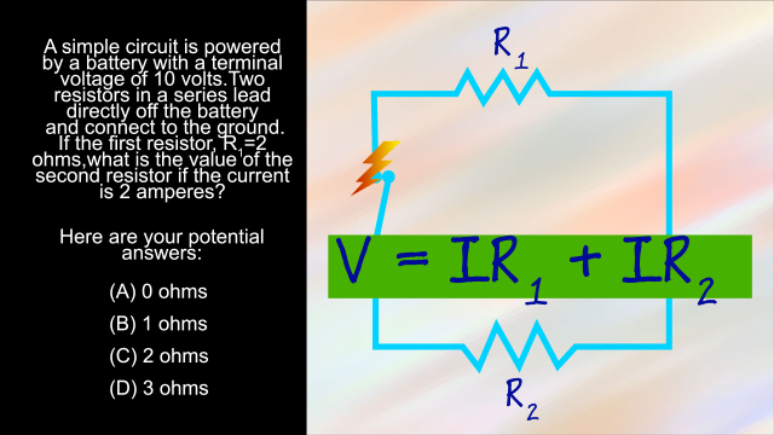
AP Physics 1: 1.4 Changes and Conservation Laws. Find the current across R2.
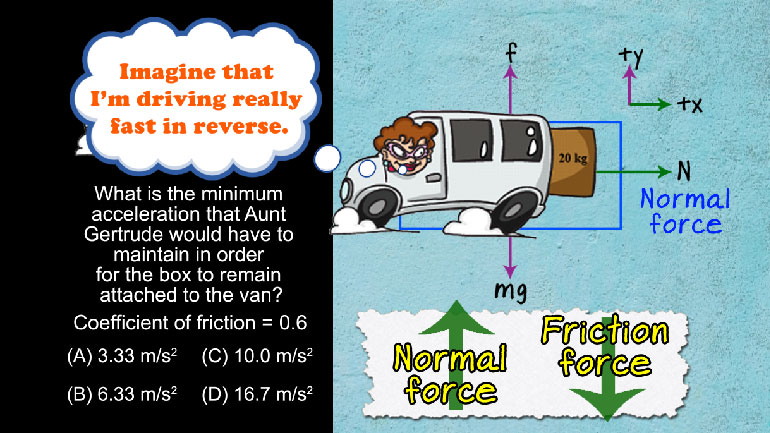
AP Physics 1: 3.4 Object Interaction and Forces 194 Views
Share It!
Description:
Sure, we can calculate force, as long as we get to stay safely away from the giant death trap elevator. You have fun up there, though.
Transcript
- 00:03
Alright here's your shmoop du jour brought to you by skyscrapers their [Skyscrapers in Chicago city]
- 00:06
impressive feats of engineering and we love to look at them you know with our
- 00:09
feet planted firmly on the ground the Willis Tower in Chicago is the tallest
- 00:13
building in the U.S. at 527 meters the 1,700 feet to reach the top floors [Willis Tower shown to be 1,729 feet]
- 00:21
tourists take a one-minute trip up an elevator that quickly accelerates to a
Full Transcript
- 00:26
high speed and intrepid schmooper weighs himself before getting on the elevator [Shmoop employee weighing himself before getting on the elevator]
- 00:30
and finds that the scale reads 500 n Newtons as the elevator begins its ascent
- 00:36
at constant acceleration he sees that the scale reads 950 Newton if the [Scale reading 950 N]
- 00:43
elevator descends with a constant acceleration equal to 1/2 the upward
- 00:49
acceleration what will the scale read on the ride
- 00:52
down and here are the potential answers... ok well we're dealing with three
- 00:58
separate forces here we have the normal force before we're even on the elevator [Luke Skywalker fighting Darth Vader]
- 01:02
the force when we're moving up in the elevator and the force when we're going
- 01:06
down all right well let's deal with the normal force first when we're on the
- 01:10
ground gravity pushes us down and the floor pushes us up these two forces [Gravity pushing down and the floor pushing up on a woman]
- 01:14
balance each other out.. if they didn't we'd float above the floor or crash
- 01:19
through it'd be kind of cool we're happy to report that the Willis Tower
- 01:22
has very sturdy floors that push back against gravity and we don't see anyone [Man stood in a glass window looking down from a skyscraper]
- 01:27
floating in Chicago so it appears the forces balance out so all this means
- 01:31
that the normal force minus mass times gravity equals zero well we're in luck
- 01:36
because we know the amount of force pushing down on the schmooper is 500 [White ball lands on 29 black on a roulette wheel]
- 01:40
Newtons and we can calculate his mass since mass times gravity equals Newtons
- 01:45
we can rearrange the equation so we have mass equals Newton's divided by gravity
- 01:50
for our sake here we'll also round gravity up to ten meters a second
- 01:55
squared when we plug in the numbers we find that his mass is 50 kilograms now [Re-arranged equation to find the mass]
- 02:00
when the elevator starts going up the force of gravity is still balanced out
- 02:03
by the force of the elevator floor but this time instead of equaling zero the [Man going up an elevator in the tower]
- 02:08
forces interact to equal mass times acceleration upwards all right well now
- 02:13
we can solve for upward acceleration all we have to do is subtract mass times
- 02:18
gravity from Newtons on the upward ride and divide that by mass okay some quick
- 02:23
calculations and we'll find that acceleration upward is nine meters per [Equation for acceleration upward shown as 9 meters per second squared]
- 02:27
second squared now we know that when the elevator starts slowing down the downward
- 02:32
acceleration is half of the upward acceleration well the downward force
- 02:36
equals negative mass times acceleration and downward acceleration equals
- 02:42
one-half of upward acceleration so the downward force minus mass times gravity
- 02:47
equals negative mass times half of upward acceleration all right we're
- 02:52
almost there I promise now we solve for the downward force which again equals [Woman waving her finger]
- 02:56
mass times gravity minus mass times one-half upward acceleration well we
- 03:01
multiply 50 kilograms by five point five meters per second squared and we get an
- 03:05
answer of 275 Newtons so the correct answer is option C let's quickly touch
- 03:11
on the other answer choices we could have knocked a and D out of the running [Boy on his phone gesturing at his laptop screen]
- 03:14
right away we know that there's a downward force in action here since
- 03:18
gravity never stops so there's no way a is correct and we know that the force [Young girls jumping up and down]
- 03:22
during the slowdown will be less than the force standing in place on the
- 03:27
ground so D would never work either and we also know that next time we go to [Man attempts to float in mid-air and falls down]
- 03:31
Chicago we'll stick to ground level attractions a super tall building in a
- 03:35
place called the windy city, yeah we don't even like to climb step ladders [Man looking up at Willis Tower with a step ladder]
- 03:39
and look out below....whoa boy!
Related Videos
AP Physics 1: 2.5 Changes and Conservation Law. At what point(s) in this situation is energy lost in any form?
AP Physics 1: 1.4 Waves. Which of the following is technically true for Max as he stands at the edge of oblivion?
AP Physics 1: 1.4 Changes and Conservation Laws. Find the current across R2.
AP Physics 1: 2.4 Changes and Conservation Laws. Which of the following circuits should the students use?
AP Physics 1: 1.5 Waves. What can possibly occur when the two waves reach each other?