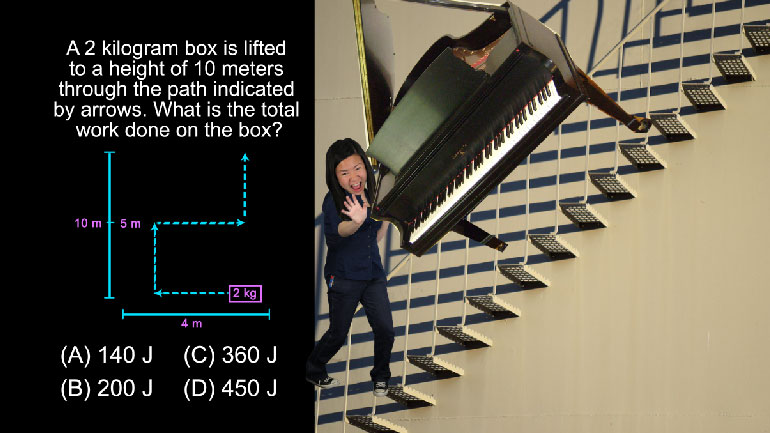
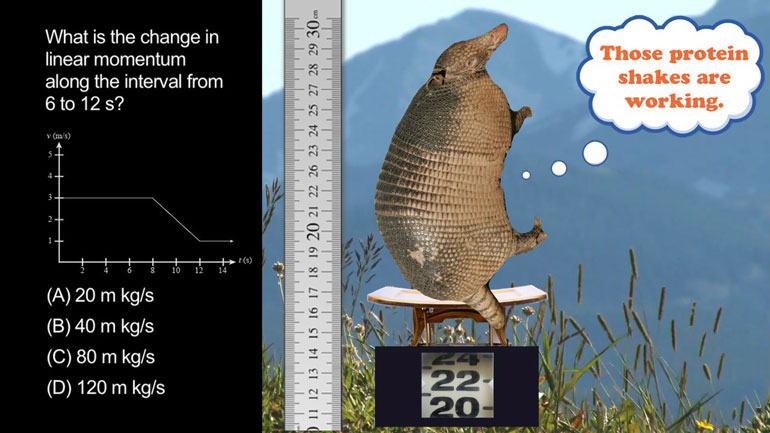
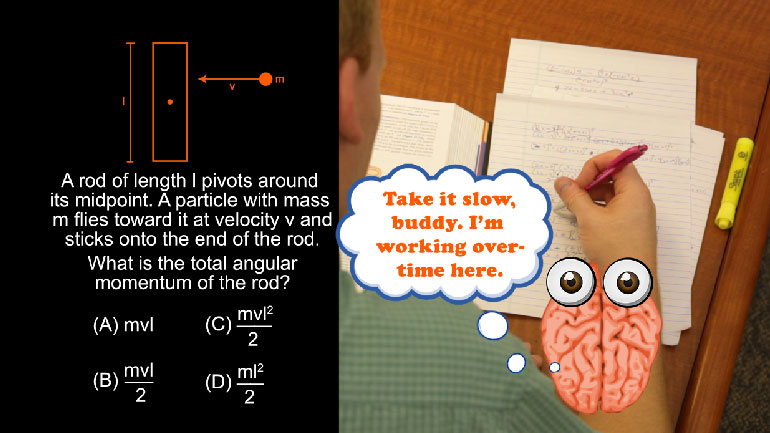
ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
AP Physics 1 Videos 86 videos
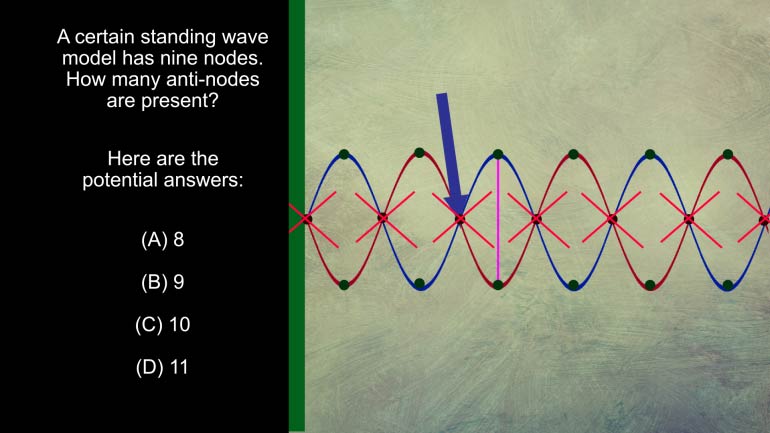
AP Physics 1: 1.4 Waves. Which of the following is technically true for Max as he stands at the edge of oblivion?
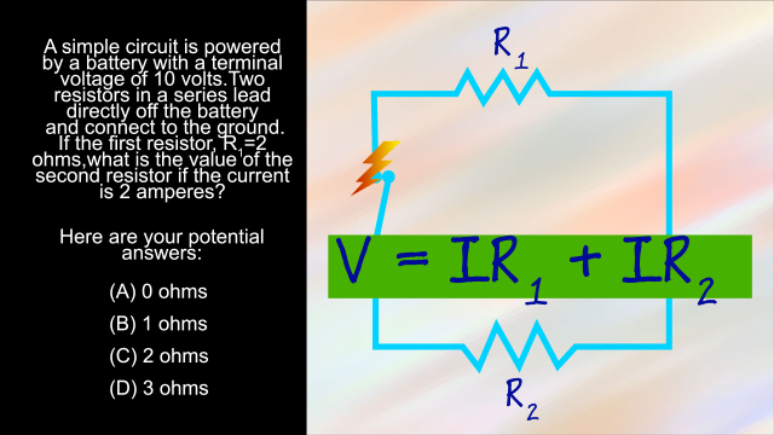
AP Physics 1: 1.4 Changes and Conservation Laws. Find the current across R2.
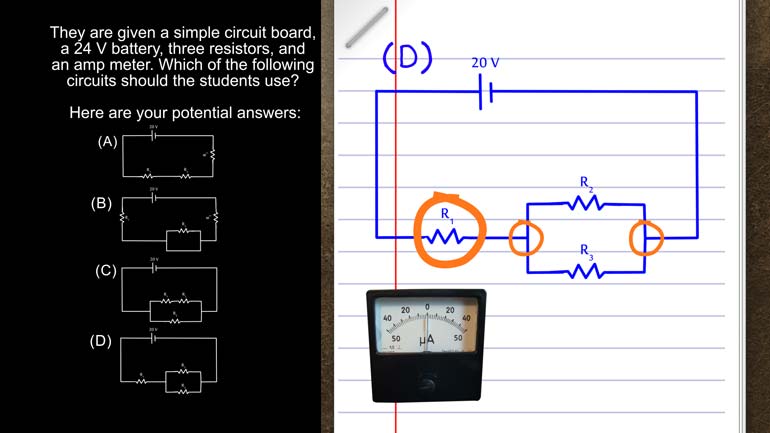
AP Physics 1: 2.4 Changes and Conservation Laws. Which of the following circuits should the students use?
AP Physics 1: 2.1 Changes and Conservation Laws 171 Views
Share It!
Description:
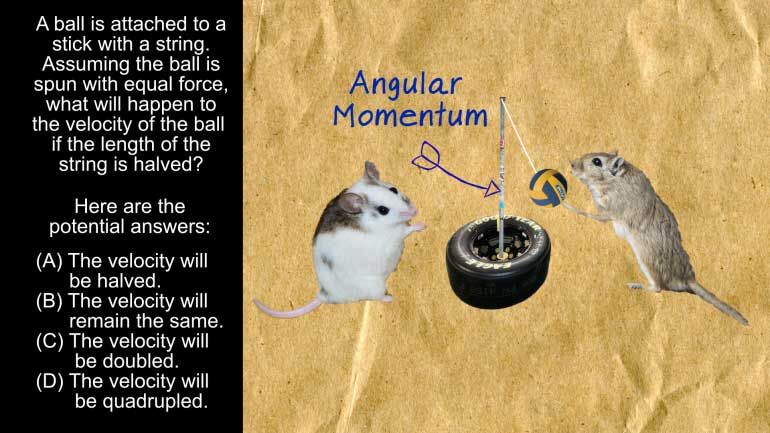
AP Physics 1: 2.1 Changes and Conservation Laws. What will happen to the velocity of the ball if the length of the string is halved?
Transcript
- 00:00
Hurry And here's your shmoop du jour Brought to you
- 00:05
by a ball tied to a stick with a string
- 00:07
Yep because without that how are the mice gonna play
- 00:10
tether ball if they do falling diagram right balls attached
- 00:14
to a string with a string assuming the ball is
Full Transcript
- 00:17
spun with equal force what will happen to the velocity
- 00:21
of the ball if the length of the string is
- 00:23
have And here the potential answers All right equal forces
- 00:27
Well that's Really important Okay so let's think about angular
- 00:31
momenta Angular momentum is the amount of rotation object has
- 00:35
mathematically speaking Angular momentum is the product of mass velocity
- 00:39
and distance from the centre which we can think of
- 00:41
as the objects radius good word and the our baby
- 00:46
And we know once mo mentum starts it won't stop
- 00:49
or change until something acts to change it that's the
- 00:52
law of conservation of momentum That's what nunes first laws
- 00:56
all about an object in motion stays in motion until
- 00:59
something acts on it and rotating or orbiting objects have
- 01:03
their own law of conservation of angular momentum The idea
- 01:06
is the same No angular momentum doesn't change unless it
- 01:10
has To just like us with socks way Don't change
- 01:13
him unless we have to get pretty pungent by your
- 01:16
laundry day So if an object momentum doesn't change unless
- 01:19
something acts upon it well what happens if the object
- 01:22
itself changes We'll answer that by talking about our favorite
- 01:26
sport figure skating We get so hyped about the winter
- 01:29
olympics and every four years you start dressing like ice
- 01:31
dancers just to get into the spirit All right well
- 01:34
we especially love when a figure skater starts twirling around
- 01:37
and then she goes faster and faster and we get
- 01:39
dizzy just looking at her The reason she picks up
- 01:42
speed is because she changes her radius She starts spinning
- 01:45
with a certain momentum and she has her arms out
- 01:48
wide like that A speeder spin She brings her arms
- 01:51
and is close to her body She can decreasing her
- 01:54
radius Her velocity than increases that's because the angular momentum
- 02:00
has to remain the same and her mass isn't changing
- 02:03
So if one part of the equation decreases another part
- 02:07
has to increase So now let's take a look at
- 02:09
our question If the force applied to the ball is
- 02:11
the same that means the angular momentum has to be
- 02:15
the same too So if we cut the length in
- 02:17
half the rest of the equation has to double The
- 02:20
mass of the ball isn't changing so the velocity will
- 02:23
have to double means going to spin around twice as
- 02:25
fast It means the right answer is c Now we're
- 02:28
going to get back to our rodent tether ball match
- 02:30
It's super cute toe watch But sometimes steve the mouth 00:02:33.603 --> [endTime] can be a real sore loser
Related Videos
AP Physics 1: 2.5 Changes and Conservation Law. At what point(s) in this situation is energy lost in any form?
AP Physics 1: 1.4 Waves. Which of the following is technically true for Max as he stands at the edge of oblivion?
AP Physics 1: 1.4 Changes and Conservation Laws. Find the current across R2.
AP Physics 1: 2.4 Changes and Conservation Laws. Which of the following circuits should the students use?
AP Physics 1: 1.5 Waves. What can possibly occur when the two waves reach each other?