ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
Chemical and Physical Properties from Structure and Arrangement Videos 10 videos
AP Chemistry 2.5 Structure and Arrangement of Atoms. Under which of the following conditions would a real gas behave more like an ideal gas?
AP Chemistry 3.5 Structure and Arrangement of Atoms. Which of the following is true regarding solids?
AP Chemistry 3.1 Structure and Arrangement of Atoms 19 Views
Share It!
Description:
AP Chemistry 3.1 Structure and Arrangement of Atoms. Which substance exhibits the weakest intermolecular forces and possibly the lowest boiling point?
Transcript
- 00:04
And here's your Shmoop du jour, brought to you by the force. [Girl using the force at a birthday party]
- 00:07
Nifty party trick, but not a good explanation tactic on exams…
- 00:13
Here's our question….
- 00:14
The boiling point for a covalent compound can be predicted by understanding intermolecular
- 00:19
forces. Which substance below exhibits the weakest intermolecular forces and possibly
Full Transcript
- 00:25
the lowest boiling point?
- 00:28
Alright. Well, the question writer threw us a bone by telling us that the substance with [Men fighting over a bone]
- 00:36
the weakest intermolecular forces will have the lowest boiling point.
- 00:41
So all we have to do is figure out which substance has the weakest forces between its molecules.
- 00:47
How do we do this?
- 00:48
Use the forceeee…
- 00:54
All intermolecular forces are ultimately just an attraction between a positive charge and [Positive and negative charge connected with love heart]
- 01:00
a negative charge, but the type of molecule will dictate how much charge is involved.
- 01:06
The more charge, the more attraction.
- 01:08
There are essentially four strengths of charge interactions that we can rank.
- 01:12
The strongest is ionic bonding, because it involves attractions between ions that have
- 01:18
at least one full positive or negative charge. [Ions attract each other from sodium and chlorine]
- 01:21
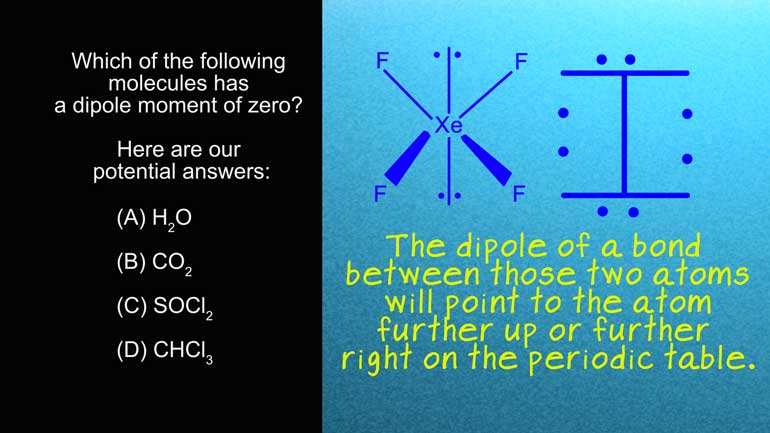
Another type of fairly strong interaction is a dipole interaction. A dipole interaction
- 01:27
occurs when a molecule has a bond dipole between a very electronegative atom, and a less electronegative
- 01:33
atom.
- 01:34
This strong dipole creates a partial positive charge on the less electronegative atom and
- 01:38
a partial negative charge on the more electronegative atom.
- 01:41
The partial negative charges are attracted to the partial positive charges, making the [Example of normal dipole interaction]
- 01:46
molecules stick together, but not as tightly as if they were full charges.
- 01:51
So…maybe not the molecules you want on your side in a rumble… [Ionic bonds fighting a dipole]
- 01:56
Any dipole in a molecule will do this, but hydrogen bonding is a special case in which
- 02:01
these interactions are particularly strong. [Hydrogen bonds in a cup of water]
- 02:03
A hydrogen bond is a dipole interaction that occurs in a molecule that has hydrogen atoms
- 02:08
bonded to a very electronegative atom, typically oxygen or nitrogen like the example shown
- 02:14
here.
- 02:15
Here’s what’s on our list so far: There’s one last force to consider. Electrons
- 02:24
in a molecule can move around and shift their charge density. This can cause more of the [Electrons moving around in a molecule]
- 02:28
negative charges of electrons in a molecule to temporarily end up on one side of the molecule,
- 02:34
leaving that side slightly negatively charged and the other side slightly positively charged
- 02:40
for a brief instant in time. The negatively charged side of one molecule can attract the
- 02:45
positively charged side of another, and the bigger the molecule, the greater the area
- 02:49
over which this attraction occurs and the stronger it is. [Lots of molecules with negatively charged electrons]
- 02:53
These attractive forces are very weak for one important reason:
- 02:56
The unbalanced charge lasts less time than it takes to jump to hyperspace. [Spacecraft jumps through hyperspace]
- 03:02
So here's our final lineup of forces:
- 03:11
Now we need to figure out what forces are holding together the molecules in the question..
- 03:15
We can get through this at light speed. [Spaceship appears]
- 03:16
H2O and BF3
- 03:19
both have dipoles, but H2O can make hydrogen bond, while BF3 sadly cannot.
- 03:25
That means H2O has the strongest intermolecular forces, followed closely by BF3. [H2O rocket wins race ahead of BF3]
- 03:31
Both CO2 and SeO2 only have London Dispersion Forces, but CO2 is smaller than SeO2, so that's that... Carbon
- 03:41
is higher on the periodic table, therefore smaller than selenium, so the forces holding [Carbon and selenium circled on periodic table]
- 03:45
it together are weaker.
- 03:46
So to make a very long story short, the answer to the question is C. Small, but proud. [Darth Vader points to answer C]
- 03:52
Much like a wise little green dude we know…
- 03:54
The right answer, C is…used the force, we did… [Yoda makes Darth Vader disappear]
Related Videos
AP Chemistry 1.3 Chemical Reaction Rates. What is the overall order of the reaction?
AP Chemistry 1.4 Chemical Reaction Rates. What are the correct units for a second order rate constant?
AP Chemistry 1.5 Chemical Reaction Rates. What is the rate law for the reaction?
AP Chemistry 3.2 Laws of Thermodynamics. What is the value for ΔG?