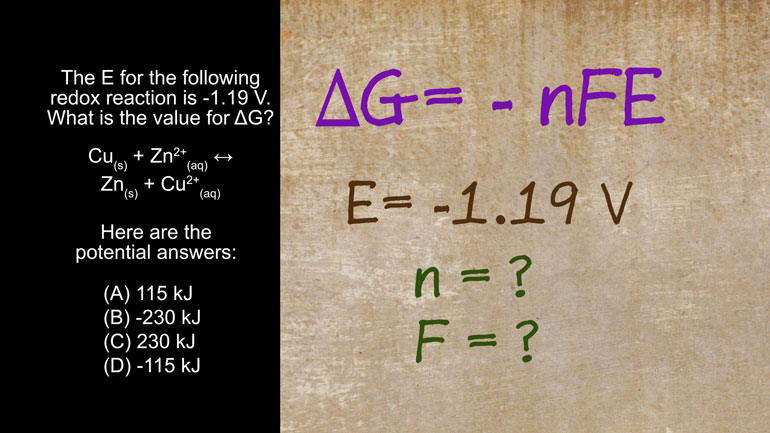ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
Chemical and Physical Properties from Structure and Arrangement Videos 10 videos
AP Chemistry 2.5 Structure and Arrangement of Atoms. Under which of the following conditions would a real gas behave more like an ideal gas?
AP Chemistry 3.5 Structure and Arrangement of Atoms. Which of the following is true regarding solids?
AP Chemistry 2.5 Structure and Arrangement of Atoms 22 Views
Share It!
Description:
AP Chemistry 2.5 Structure and Arrangement of Atoms. Under which of the following conditions would a real gas behave more like an ideal gas?
Transcript
- 00:00
Thank you We sneak Here's your smoke do sure brought
- 00:05
to you by ideal gases if they're not ideal maybe
- 00:09
it's just a phase they're gone through and you know
- 00:11
get better over time Here's our question under which of
- 00:14
the following conditions what a real gas behave more like
Full Transcript
- 00:16
an ideal gas And here are potential answers All right
- 00:20
Well if all our ideal circumstances came true we'd ride
- 00:23
our unicorn to work as a professional nap taker and
- 00:26
collect our six figure salary at the end of the
- 00:28
day But the hard truth is ideal Circumstances are rarely
- 00:31
reality It's true in our dreams of unicorn transportation and
- 00:35
it's especially true in chemistry and ideal gas is one
- 00:38
that behaves in a predictable mathematical fashion when the temperature
- 00:40
pressure amount of gas or volume of gas changes following
- 00:44
what is called the ideal gas law pressure times volume
- 00:47
equals number of moles times a calculated gas constant our
- 00:50
times the temperature So what makes the ideal gas law
- 00:53
fail in reality forces of attraction between gas molecules When
- 00:58
gas molecules are attracted to each other they spent too
- 01:01
much time together and don't move around as much making
- 01:03
their behaviour less ideal Forces of attraction between gas molecules
- 01:08
are short range so the farther apart molecules are the
- 01:11
less powerful these forces are And if gas molecules are
- 01:14
moving around quickly they'll whiz by each other instead of
- 01:17
spending time together in giving those forces of attraction timeto
- 01:20
work in order for our molecules to be well behaved
- 01:23
we want them to have fewer forces of attraction between
- 01:26
them which means we want them to be far apart
- 01:29
and moving fast This means that the question is actually
- 01:32
asking us under which conditions will gas molecules be far
- 01:36
apart and moving fast So what does that question mean
- 01:40
by conditions Well all of the answers given pressure and
- 01:43
atmospheres and a temperature And kelvin so we know our
- 01:46
conditions will have something to do with those measurements More
- 01:49
pressure means that the molecules will be forced closer together
- 01:52
So we want a low pressure to keep them apart
- 01:55
Temperature is the average kinetic energy of the gas molecules
- 01:59
So ah hi Temperature means they have more energy and
- 02:02
will be moving faster which is what we want Well
- 02:04
answer D has the lowest pressure and the highest temperature
- 02:07
Which means it's the answer We want yeah yes it's
- 02:11
Not a terrible job to solve chemistry problems but well 00:02:14.643 --> [endTime] we'll take that professional knocker position any day
Related Videos
AP Chemistry 1.3 Chemical Reaction Rates. What is the overall order of the reaction?
AP Chemistry 1.4 Chemical Reaction Rates. What are the correct units for a second order rate constant?
AP Chemistry 1.5 Chemical Reaction Rates. What is the rate law for the reaction?
AP Chemistry 3.2 Laws of Thermodynamics. What is the value for ΔG?