ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
AP Psychology Videos 135 videos
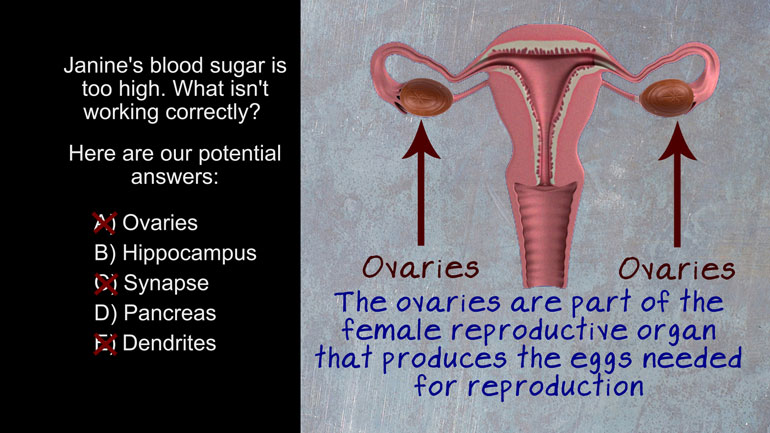
AP Psychology 2.3 Testing and Individual Differences. Which factor below needs to be considered in the administration and evaluation of the attenti...
AP Psychology 2.4 Testing and Individual Differences. Which of these is an example of studies used in the nature vs. nurture debate of intelligence?
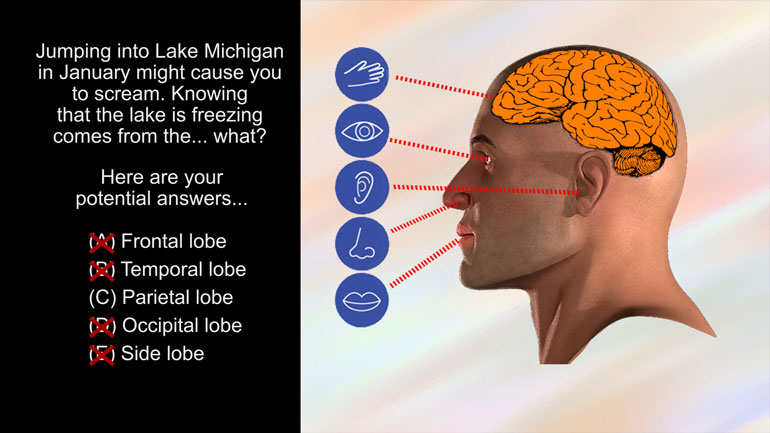
AP Psychology 1.2 Developmental Psychology. How would you respond to someone stating that babies are born without any real sense of the world aroun...
AP Psychology 2.5 Sensation and Perception 7 Views
Share It!
Description:
AP Psychology 2.5 Sensation and Perception. What is the brain's ability to interpret the same color despite changes in lighting called?
Transcript
- 00:03
Here's your shmoop du jour brought to you by art museums what [Man looking at paintings]
- 00:07
can we say we Louvre a good Art Museum alright here's today's question Susana
- 00:13
loves to visit her local museum her favorite painting is a haystack sitting [Susana looking at painting of haystack]
- 00:18
against a blue sky and it's located next to a window during different times of
- 00:23
the day the shade of the haystacks seems to change but her brain always processes
Full Transcript
- 00:27
the color as straw the ability of the brain to interpret the same color
- 00:32
despite changes in lighting is called what and here are your potential answers ....
- 00:39
well it's interesting as that whole Susana story was the real meat of the [Woman watching TV]
- 00:43
question is in the last sentence the ability of the brain to interpret the
- 00:48
same color despite changes in lighting is called what that thing well B
- 00:52
definitely isn't the one that we want The word linear doesn't
- 00:58
exactly have anything to do with color and shape actually linear perspective [Parallel lines below linear perspective]
- 01:01
refers to the depth cue we receive from parallel lines that appear to converge
- 01:05
think like you know railroad tracks and think quick that trains coming fast
- 01:10
hey speaking of lines, continuity a
- 01:13
Gestalt rule of perception most often refers to lines describing the visual
- 01:17
tendencies to create continuous figures take the lines for railroad tracks if we [Person highlighting railroad tracks]
- 01:22
were to cross them well typically we'd still see the two lines as separate
- 01:26
figures we carry the line forward even when they cross but again this is
- 01:31
totally unrelated to color in the perception of it so a nice try there [Gestalt standing with a cane]
- 01:35
Gestalt we know it must've been tough to click away from the cat videos on
- 01:39
YouTube to watch this one because we're super nice we're going to make that
- 01:42
pain a little easier to bare so look at this kitty cute huh snap, close one eye okay [A cat with one eye closed]
- 01:47
good now open that eye and close the other eye yeah you saw that little furry guy
- 01:52
slightly differently that time right well that's what's described as
- 01:56
binocular disparity and while it may have just made you look a bit goofy in [Man transforms face into goofy]
- 02:02
front of your computer screen it's also not what we're looking for all right
- 02:05
say goodbye to fluffy only temporarily, we promise so that leaves us with C and E
- 02:09
okay so we all know what an optical illusion is it's this and this and this [Examples of optical illusions]
- 02:14
it's fun to play around with but not our answer but there is a great optical
- 02:19
illusion that illustrates the correct answer C - brightness constancy take a
- 02:24
look at this image compare the colors of the checkers mark a and B do they look
- 02:29
different too yes probably but they're not ooh spooky
- 02:32
your brain is contextualizing the colors based on the perceived shadow cast from
- 02:37
the green cylinder which is directly toying with the concept of brightness [Checkers board with a green cyclinder]
- 02:41
constancy well brightness constancy describes how despite the change of
- 02:46
light condition we always perceive colors the same way in other words our
- 02:50
brains adapt and alter our perceptions based on the lighting conditions around
- 02:55
us taking into account light sources and shadows which is exactly what the
- 02:59
question describes and now that we finished this question let's resume [Man watching cat videos]
- 03:03
which should always be our regularly scheduled programming cute little kitty...
Related Videos
AP Psychology 1.1 Sensation and Perception. The process by which the brain can turn sensory stimuli from the outside world into electrical signals...
AP Psychology 1.1 States of Consciousness. Who conducted research on REM sleep deprivations?
AP Psychology 2.2 Social Psychology. Which of the following was an independent variable manipulated in Asch's research?
AP Psychology 1.1 Personality. According to Freud, these three parts of personality are constantly in conflict.
AP Psychology 1.1 Social Psychology. Which of the following best describes social psychology?