ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
Performing data analysis Videos 10 videos
Hi there. We'd like to wave hello to you, but the internet isn't letting us. So instead, accept this fun question about waves and physics! It's alm...
Got an AP test lurking around the corner? Good thing we brought this handy slingshot and some sweet math.
It takes a tiny village to build a tiny renewable energy source.
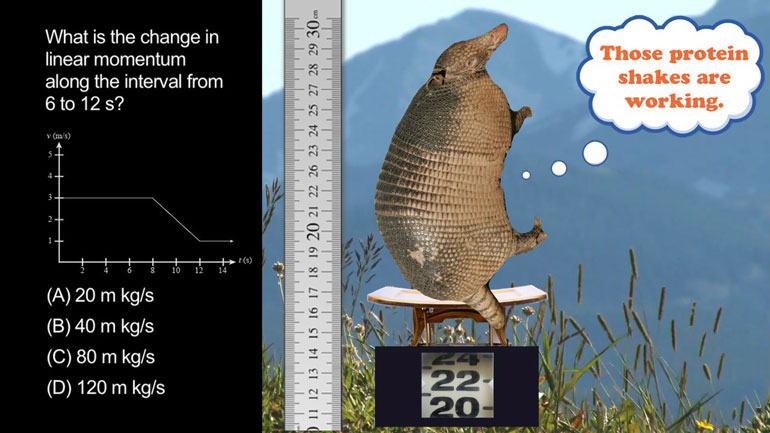
AP Physics 1: 3.2 System Interactions and Changes 182 Views
Share It!
Description:
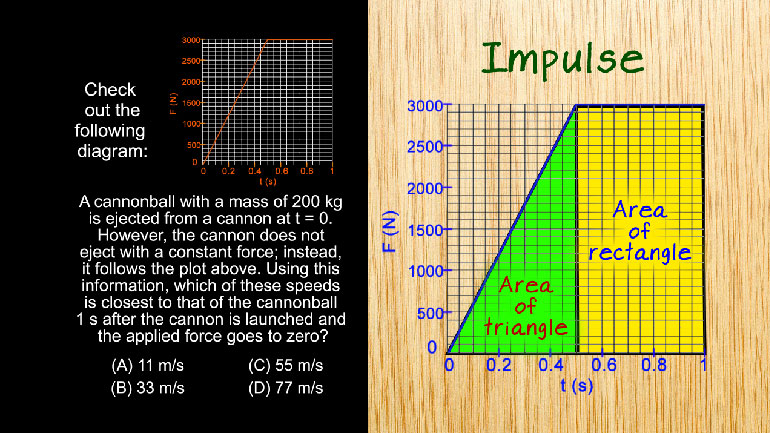
AP Physics 1: 3.2 System Interactions and Changes. Which of the following is closest to the cannonball's speed one second after launch?
Transcript
- 00:00
Thank you We sneak and here's your shmoop du jour
- 00:05
brought to you by cannon balls They're capable of great
- 00:08
destructive force and are also our favorite way to enter
- 00:11
the swimming pool I checked the following diagram Alright a
- 00:15
cannonball with a mass of two hundred kilograms is ejected
Full Transcript
- 00:19
from a cannon at t equals zero However the cannon
- 00:22
does not object with a constant force Instead it follows
- 00:25
the plot above using this information which of these speeds
- 00:29
is closest to that of the cannon ball One second
- 00:33
after the cannon is launched and the applied force goes
- 00:37
to zero All right And here the potential answer who
- 00:40
Good question Ah forced time graph We remember back when
- 00:45
we were young and saw forced time grab for the
- 00:47
first time It was new and scary Now that we're
- 00:50
old and withered We know how to make it work
- 00:52
for us right Well when we see this graph we
- 00:54
know we're dealing with impulse impulses The change in mo
- 00:57
mentum over an interval of time and mo mentum is
- 01:00
equal to mass times the change of velocity To find
- 01:05
the impulse using our force time graph we need to
- 01:07
figure out the area under the curve In our graph
- 01:10
here we could break it into two parts a triangle
- 01:13
and a rectangle Then we calculate the area of each
- 01:16
shape Well we'll tackle the triangle first To get that
- 01:18
we use the formula of one half base times height
- 01:21
Shmoop And then we'll take the area of the rectangle
- 01:27
base times height Well if we add them together we
- 01:33
get a total impulse of two thousand two hundred fifty
- 01:36
newton seconds All right because we now know the impulse
- 01:39
we can plug in our numbers and solve for velocity
- 01:42
right ankle Sometimes be i get to hand him over
- 01:46
to kilograms Let me point you alright so all we
- 01:50
have to do is around eleven point two five down
- 01:52
to eleven and will arrive at our answer option A 00:01:54.72 --> [endTime] That wasn't too bad We owe you
Related Videos
AP Physics 1: 2.5 Changes and Conservation Law. At what point(s) in this situation is energy lost in any form?
AP Physics 1: 1.4 Waves. Which of the following is technically true for Max as he stands at the edge of oblivion?
AP Physics 1: 1.4 Changes and Conservation Laws. Find the current across R2.
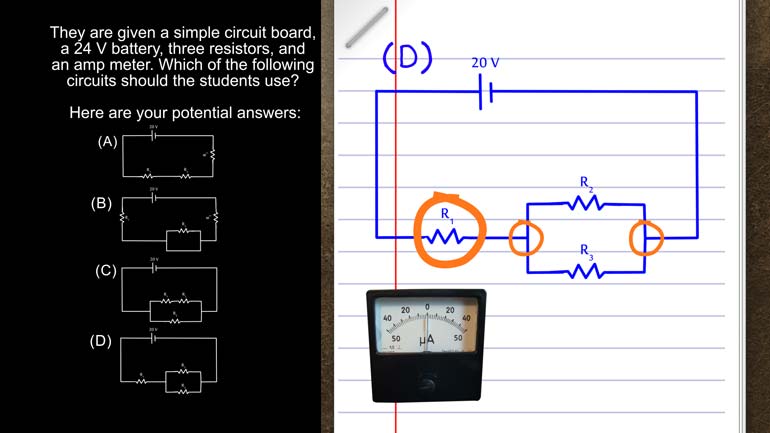
AP Physics 1: 2.4 Changes and Conservation Laws. Which of the following circuits should the students use?
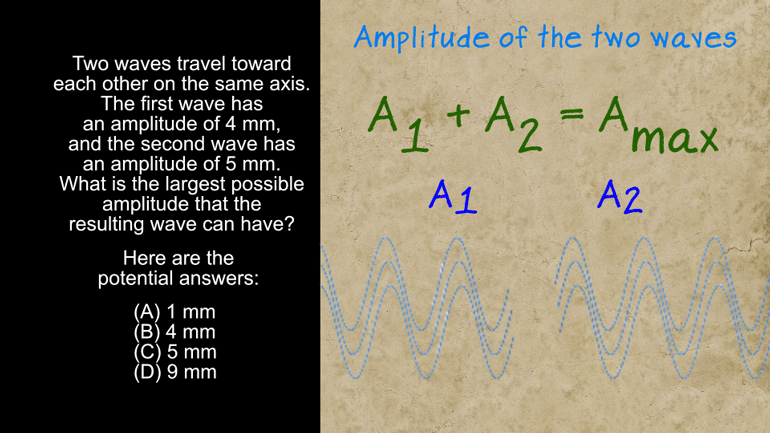
AP Physics 1: 1.5 Waves. What can possibly occur when the two waves reach each other?