ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
AP Physics 2 Videos 66 videos
AP Physics 2: 1.1 Properties of Objects and Systems. What is the magnitude and direction of the conventional current in this wire?
AP Physics 2: 1.5 Properties of Objects and Systems 170 Views
Share It!
Description:
AP Physics 2: 1.5 Properties of Objects and Systems. According to the Bohr's model of the atom, which of the following are true?
Transcript
- 00:00
Look And here's your shmoop du jour brought to you
- 00:04
by electron liberation which sounds like the tiniest political movement
- 00:09
in the universe according to bores Model of the atom
- 00:14
Which of the following is true Select two answers And
- 00:18
here the potential answers All right four meals Simon energy
Full Transcript
- 00:26
All right well niels bohr was a huge contributor to
- 00:28
our understanding of the physical world he also founded What's
- 00:31
now known as neil's bohr institute could be a little
- 00:35
weird taking a class from someone called professor board Though
- 00:39
boris model of the atom is still one of the
- 00:41
best ways to think about and visualize these sub sub
- 00:45
sub microscopic particles The bohr model describes how electrons orbit
- 00:50
the nucleus of an atom Electrons orbited different levels We
- 00:54
didn't think of it like our solar system where the
- 00:56
planet's orbit at different distances from the sun The different
- 00:59
orbital distances in adam are set based on the energy
- 01:02
level of the electrons that well closer to the nucleus
- 01:06
Electrons are in lower energy orbits so it takes more
- 01:10
energy to move them away from the nucleus I didn't
- 01:13
get sucked in let's Look at this diagram of hypothetical
- 01:16
energy levels in an adam we can see that it
- 01:19
takes more energy to move an electron from the lowest
- 01:22
orbit to the point where it's completely liberated from the
- 01:25
atom than it does to move an electron from a
- 01:27
higher orbit So this means aids incorrect now One electron
- 01:32
is in a higher energy state and then loses energy
- 01:36
It moves back down bolstered of the nucleus like that
- 01:40
And when this happens the electron beam it's a faux
- 01:42
thanh like shooting off a flare gun as it's running
- 01:45
out of gas The wavelength of that proton is related
- 01:52
to the change in energy of the electron The smaller
- 01:55
the change in energy the longer the wavelength Well the
- 01:58
wavelength of the admitted photons equals planks Constant times The
- 02:02
speed of light divided by the change in energy equation
- 02:06
looks like that the equation here place constant is represented
- 02:09
by age Now remember that diagram we saw earlier with
- 02:13
the energy level thing Yeah let's Look at it again
- 02:15
We can see that the biggest difference in energy is
- 02:18
between the first and second level's Answer b says that
- 02:22
the longest wavelength of photons can have is between any
- 02:25
calls to an n equals one levels They're looking at
- 02:28
the diagram We can see there's no way that's true
- 02:30
largest difference in energy is between the n equals one
- 02:33
and n equals two levels so that it mean the
- 02:35
resulting photons would have the shortest wavelength The answer is
- 02:40
incorrect also Okay we're making progress We know what the
- 02:44
wrong answers are And being smarties were able to deduce
- 02:47
that the right answer here is see andy but just
- 02:50
for fun Let's figure out why they're right And yet
- 02:52
we know our idea of funds Little weird All right
- 02:56
Answer c says that the energy required to liberate an
- 02:58
electron from the end energy level is different for all
- 03:01
atoms of different elements With only one electron Well the
- 03:04
formula to calculate the amount of energy needed A liberating
- 03:07
electron is the atomic number over the energy level times
- 03:10
negative thirteen point six electron volts that's the equation right
- 03:13
there Because adam's all have a different atomic number based
- 03:17
on the number of protons in their nuclei the energy
- 03:20
level will always be different And answer D states the
- 03:23
energy required to liberate an electron from a smaller radius
- 03:26
Orbit is larger than for a large radius orbit Right
- 03:31
Well this matches what we've already seen in our electron
- 03:33
level diagram this thing after all an electron closer to
- 03:37
the nucleus will have a smaller orbital radius Like how
- 03:40
mercury has a smaller orbital radius around the sun And
- 03:44
we do on earth Well these atomic structures look simple
- 03:47
but as physicists we know that nothing is as simple
- 03:50
as it looks A lot going on even the tiniest
- 03:52
of systems But there aren't subatomic politics That would just
- 03:56
be silly Which is a good thing because in a 00:03:58.17 --> [endTime] particle campaign election electrons would always go negative
Related Videos
AP Physics 2: 1.1 Properties of Objects and Systems. What is the magnitude and direction of the conventional current in this wire?
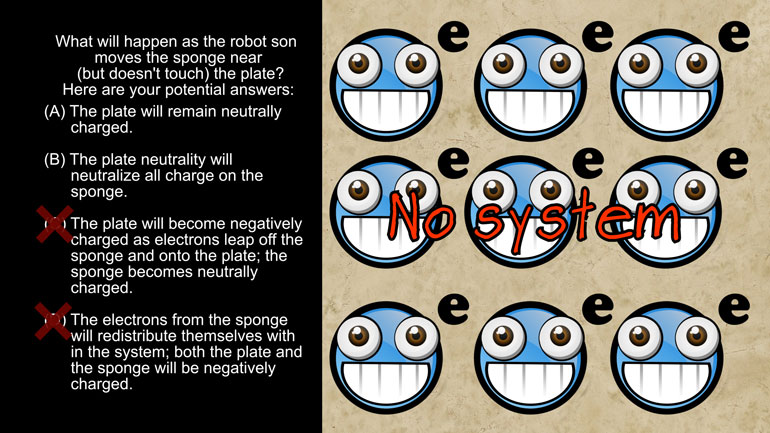
AP Physics 2: 2.2 Properties of Objects and Systems. What will happen as the robot son moves the sponge near (but doesn't touch) the plate?
AP Physics 2: 2.4 Properties of Objects and Systems. How could you show the carnival barker an emission spectrum?
AP Physics 2: 1.4 Object Interaction and Forces. What is the approximate value of nickel-62's binding energy per nucleon?