ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
Waves and Optics Videos 2 videos
AP Physics B: Waves and Optics Drill 1, Problem 1. Which of the following is technically true for Max as he stands still at the edge of oblivion?
AP Physics 2: 1.1 Properties of Objects and Systems 190 Views
Share It!
Description:
AP Physics 2: 1.1 Properties of Objects and Systems. What is the magnitude and direction of the conventional current in this wire?
Transcript
- 00:00
Hurry And here's your smoke too Sure brought to you
- 00:05
by day dreams We don't daydream We maintain focus at
- 00:09
all times and never let our imaginations run away Because
- 00:11
we're always dedicated Tio What was that Sorry Drifted away
- 00:16
there from all right Tear the following passage and image
Full Transcript
- 00:19
Here we go jakes learning about electric current in class
- 00:22
But the monotonous voice of the teacher sends jake into
- 00:24
a daydream Imagine shrinking down to the size of an
- 00:29
electron In exploring the wire jake abruptly wakes up when
- 00:33
his teacher asked him are you paying attention Howto electrons
- 00:36
behave Jake replies Well they're pretty cool They go with
- 00:39
the flow in his dream when a potential difference is
- 00:43
set up across the ends of the wire jake and
- 00:45
the electrons all started bumping along in the same direction
- 00:50
The current the wires calculated with the equation i equals
- 00:53
nada que where N is the number of charged particles
- 00:57
per unit Volume is the cross sectional area of the
- 01:01
wire is the drift velocity of the particles and cue
- 01:05
is the charge on each particle brought to you by
- 01:08
american express Yeah All right The cylindrical wire above has
- 01:12
a radius of zero point five millimeters The electrons have
- 01:15
a speed of be equals one millimeters per second and
- 01:18
a density of unequal six times ten to the twenty
- 01:20
eight meters to the negative third what's the magnitude and
- 01:24
direction of the conventional current in this wire and hear
- 01:28
the potential answers all right Interesting Well when we daydream
- 01:32
were usually in a spaceship headed to mars not wearing
- 01:35
clothes or we're making the winning shot at the buzzer
- 01:37
Yeah like that We don't dream about being an electron
- 01:40
and a wire but we don't judge jake here he's
- 01:42
going to solve the world's problems and we're grateful were
- 01:46
given most of what we need here were given number
- 01:48
of particles see were given the radius of the wire
- 01:52
And with that we were able to find the area
- 01:54
of the cross section with a little old school gym
- 01:56
called pi r squared remember that didi Yeah area and
- 02:01
because we're dealing with some crazy big numbers will make
- 02:04
it a little easier on ourselves and round pie down
- 02:06
to three Oh and will express the radius in meters
- 02:10
rather than millimeters keep everything in the same firm we're
- 02:14
given The drift velocity which is one millimeter per second
- 02:18
or one meter times ten to the negative third per
- 02:20
second We're not given the charge of each particle but
- 02:23
we know that we're dealing with electrons Electrons are teeny
- 02:26
tiny little particles with a tv tiny electrical charge Their
- 02:30
charges so tiny in fact that they produce the smallest
- 02:33
possible unit of charge called the elementary charge or just
- 02:37
eat elementary charge is produced by protons and electrons The
- 02:41
proton is all smiles with a positive elementary charged electrons
- 02:46
so they don't go in for all that positive attitude
- 02:48
stuff they're always negative Negative negative twenty four seven Yeah
- 02:52
like that real downer Sad mood The elementary charge of
- 02:55
one electron is one point six two one seven six
- 02:58
five seven times ten to the negative nineteen who longs
- 03:03
Yeah but like electricity we try to take the path
- 03:06
of least resistance So we'll round that up to times
- 03:09
ten to the negative nineteenth Cool Okay we've got our
- 03:12
numbers and we can plug him into our equations Quick
- 03:14
reminder Current equals the number of charged particles per unit
- 03:18
of volume times the cross sectional area of the wire
- 03:21
times The drift velocity the particles times the charge of
- 03:24
each particle Got that Now if you think and we
- 03:27
have our density six times ten to the twenty eighth
- 03:29
meters to the negative third we have our area three
- 03:32
times point five times ten to the negative Thirty meters
- 03:34
squared You have our velocity one meter times ten to
- 03:37
the negative Third per second And we have our charge
- 03:40
two times ten to the negative nineteenth cool arms putting
- 03:42
in the numbers just looks like this and it's pretty
- 03:45
ugly And we can clean that up a little by
- 03:47
taking care of the square in the middle making the
- 03:49
area equal three times point two five times ten to
- 03:52
the negative six meters square And when we do the
- 03:55
math or have our fancy pants calculated to the mat
- 03:58
for us we come up with an answer of a
- 04:00
charge of nine films per second A nine amps Look
- 04:04
at us making progress All right One last part of
- 04:07
the puzzle is knowing which direction the current is going
- 04:09
in this wire We're dealing in terms of conventional charge
- 04:13
which assumes the charge is positive Well positive charge moves
- 04:16
from higher potential towards lower potential Those since a has
- 04:20
a higher potential than be the conventional current is making
- 04:23
a beeline towards b b line and say we did
- 04:26
there get it pretty good All right now if we're
- 04:29
talking in terms of electron flow it'd be the opposite
- 04:31
But we're not talking about electron flow so don't sweat
- 04:34
that right now after all of this were able to
- 04:36
definitively state that the answer is there's A current of
- 04:39
nine amps headed towards you shouldn't worry if we daydream
- 04:43
little it's actually an important part of the scientific process
- 04:45
It also prepare us for a nobel prize speech Yeah 00:04:48.867 --> [endTime] now that's some great daydreaming
Related Videos
AP Physics 2: 1.5 Properties of Objects and Systems. According to the Bohr's model of the atom, which of the following are true?
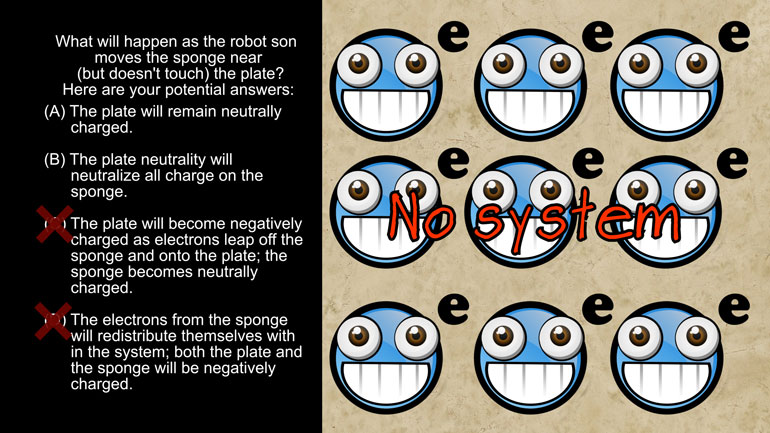
AP Physics 2: 2.2 Properties of Objects and Systems. What will happen as the robot son moves the sponge near (but doesn't touch) the plate?
AP Physics 2: 2.4 Properties of Objects and Systems. How could you show the carnival barker an emission spectrum?
AP Physics 2: 1.4 Object Interaction and Forces. What is the approximate value of nickel-62's binding energy per nucleon?