ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
AP Biology 2.1 Essential Life Process Information 4 Views
Share It!
Description:
AP Biology 2.1 Essential Life Process Information. What is the simplest interpretation of the results?
Transcript
- 00:04
And here's your Shmoop du jour, brought to you by genotypes.
- 00:07
Now available in relaxed fit, bootcut, and skinny leg. [Genotypes wearing variations of jeans]
- 00:10
Okay, here's our question…
- 00:12
A bird with gray feathers mates with a bird that also has gray feathers.
- 00:15
They have 4 offspring with white feathers, 9 with gray feathers, and 4 with black feathers. [Birds flying together]
Full Transcript
- 00:22
What is the simplest interpretation for these results?
- 00:24
Here are the potential answers…
- 00:27
Okay, here we go.
- 00:30
To keep it simple, let’s first assume that feather color is a single trait under the [Bird spreading its wings]
- 00:34
control of a somatic gene on a single chromosome.
- 00:39
This already eliminates answers C and D, since dihybrid crosses involve two different traits,
- 00:44
and sex-linkage involves the two sex chromosomes, rather than the other somatic chromosomes.
- 00:50
This leaves us with options A and B. First, let’s think about what phenotypes
- 00:55
we’re seeing.
- 00:56
The phenotype is what’s physically displayed, while the genotype is what is encoded genetically. [Girl and guy looking puzzled]
- 01:01
So taking a look at this question, we see three phenotypes: black, white, and gray. [Three birds on a branch]
- 01:05
Now we need to think about what their genotypes are…
- 01:08
We're thinking bell-bottom, but…don't hold us to that. [Three phenotypes wearing jeans]
- 01:11
Since feather color is a trait controlled by a single allele, when a new baby bird is
- 01:15
born, there are three possibilities for its genotype: (1) it inherits two dominant alleles
- 01:21
– this is called “homozygous dominant” (2) it inherits a dominant and a recessive
- 01:26
allele, or “heterozygous”, or (3) it inherits two recessive alleles – called “homozygous
- 01:32
recessive”.
- 01:33
Huh.
- 01:34
Really thought "bell-bottoms" would be a choice for genotype…
- 01:36
Anyway.
- 01:37
The question is, which color is dominant?
- 01:39
Let’s assume black feathers are dominant here. [Black birds and white birds in a field]
- 01:41
If that’s the case, in a monohybrid cross, birds that are heterozygous should be black,
- 01:45
as black feathers would dominate over the gene for white feathers.
- 01:49
But we don’t see that – we see birds with gray feathers. [Black, Gray and White birds in a field]
- 01:52
This means that we are likely to have incomplete dominance – where heterozygotes show a mixture
- 01:57
of the dominant and recessive alleles for a trait.
- 01:59
Which means the answer for this question is (A).
- 02:02
Glad we came to the right answer.
- 02:03
Now we can dihybrid happy. [A gravestone for Science McScienceton]
Up Next
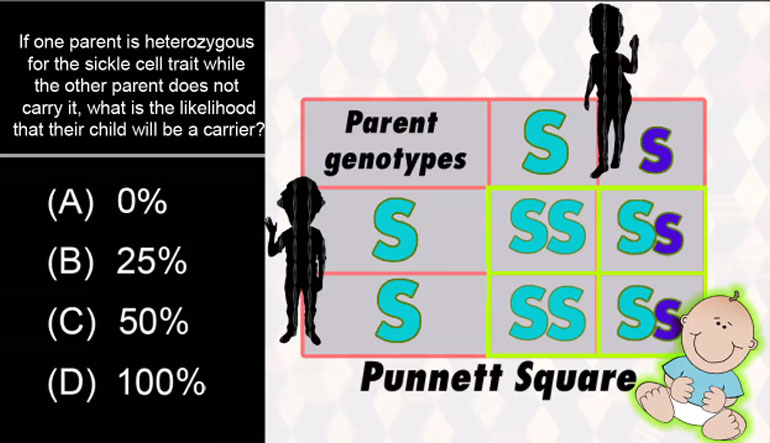
AP Biology: Essential Life Process Information Drill 1, Problem 1. If one parent is heterozygous for the sickle cell trait while the other par...
Related Videos
AP Biology: Biological System Interactions Drill 1, Problem 1. Complete the sentence about a saturated fatty acid.
AP Biology: Evolution Drives the Diversity and Unity of Life Drill 1, Problem 1. The first cells on planet Earth were likely what?
AP Biology: Free Energy and Molecular Building Blocks Drill 1, Problem 1. Which statement incorrectly describes the properties of water?
AP® Biology: Evolution Drives the Diversity and Unity of Life Drill 1, Problem 2. What was likely the first genetic material?